What is a Mortgage?
A mortgage is a legal agreement between a lender who offers financial help with interest and a borrower who makes regular monthly fees. A real asset is used as collateral to secure the loan. The effectivity of the property as guarantee becomes void at the full payment of the loan.
Any legal property including real estate and personal possessions (e.i. jewelry, automobiles) can serve as collateral as well. However, tangible assets are more commonly used.
The Right Mortgage Plan for Investors
Each investor can customize the mortgage plan to fit his or her preferences. To determine which plans are the most suitable to invest in, the primary factors to consider are the financial stability and solvency of the capitalist. The investor must have sufficient funds to meet the financial requirement of a borrower who wants to purchase a home. In addition, loan applicants also prefer to customize the mortgage plan so it’s very important that the investor and borrower are on the same page before entering into a loan agreement.
Therefore, investors must understand the essential parameters of mortgage lending. Here are some of the valuable information you need to know about investing in mortgages:
The Pre-Approval Process
The pre-approval process is a formal and extensive procedure that determines if borrowers are eligible to secure a loan. Lenders will assess the loan applicant’s gross annual income, credit standing, and assets or liabilities, among others. This process is implemented to ensure the returns on the investor’s money. Once documents are pre-approved, the chance of finding a home is easier and faster.
To proceed with the pre-approval, the following details are necessary:
- Gross Income
- Assets and Liabilities
- Credit Records
- Employment History
- Valid Identification
- Proof of Billing Address
- Social Security Number
- Other Documents
How Much Are You Willing To Lend to a Borrower?
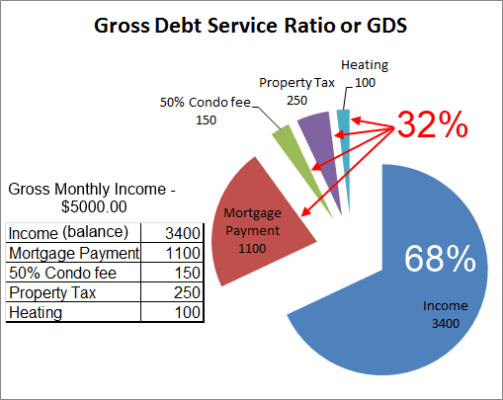
The amount that investors can lend to a borrower is determined by calculating the loan applicant’s Gross Debt Service (GDS) or Total Debt Service (GDS) ratios. The calculation of the GDS ratio includes the total property cost, interest, taxes, and other property fees. Meanwhile, TDS includes not just the housing costs (GDS), but other loans and obligation like credit card debt and car loans.
According to the Canadian Mortgages and Housing Corporation (CMHC), GDS and TDS must not exceed 35% and 42% of the monthly income, respectively. To make the calculation easier, use mortgage loan calculators to compute the amount the loan applicant can afford to borrow. Knowing this information will help you determine the amount that you are willing to lend.

The Elements of a Mortgage Loan
A mortgage loan has three basic elements: (1) mortgage terms, (2) interest rate, and (3) amortization period.
Mortgage Terms
The mortgage term refers to the duration that the parameters of a particular mortgage agreement remain in legal effect. The length of the mortgage loan can last for several months and even years. Once the mortgage matures at the end of the term, the amount loaned by the borrower must have already been paid in full. Otherwise, the borrower must renew the deal or refinance the property. Borrowers may also renegotiate while the mortgage is active, but this depends on whether the loan agreement with the lender provides for it.
There are three types of mortgage terms:
- Short-term Mortgage. According to CMHC, mortgages less than five years are short term. This type is easier to negotiate especially when revisions are necessary or interest rates swing.
- Long-term Mortgage. Long-term mortgages have a duration of more than five years, and borrowers are usually offered the same interest rates throughout the effectivity of the loan agreement. Unlike in short-term mortgages, renegotiating a long-term mortgage is very unlikely.
- Convertible-term Mortgage. These mortgage plans can be converted from a short-term to a long-term scheme. However, interest rates, the loan amount, and the details of the amortization will also change along with the conversion.
Interest Rate
The interest rate is essentially the cost of the mortgage. It is the amount the borrower owes the lender for loaning him the money to buy a house. It is based on the current rate levels in the market and has two basic types – fixed and variable.
- Fixed Interest Rate. It is the applicable rate for the entire duration of the mortgage. This rate protects the borrower from sudden market swings that affect the monthly amortization value.
- Variable Interest Rate. This rate changes along with the fluctuations in the market. As a result, unpredictable changes in rates will cause the sudden rise or fall of the amortization payments.
Amortization Period
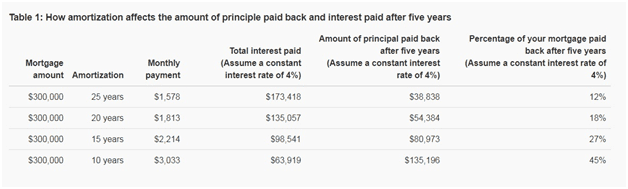
The amortization period is the length of time it takes for a loan to be fully paid. Payments are usually scheduled to be paid every month, and the amount partially covers the principal amount plus the interest and other related fees. The longer the amortization of a mortgage loan is, the costlier the monthly amortization payments of the borrower will be since the loan will keep incurring interest until the full payment of the mortgage.
The table below shows a sample of the amortization period.
What Mortgage Type Will You Choose?
Choose an investment that suits you best. Understanding the elements of a mortgage and its many types will help you make a decision. To guide you, here are the several types of mortgage plans:
Conventional Mortgage
This low-ratio mortgage needs a downpayment of 20% or more of the property’s total value. According to Loans Canada, this loan is not insured by a government agency but rather by a private lender.
High Ratio Mortgage
This type requires 20% down payment or less. The Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce stated that leading insurance groups such as the Canadian Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC), Genworth Financial, and Canada Guarantee cover this mortgage plan.
Open Mortgage
This category has a flexible scheme that locks in borrowers for shorter terms (e.g., six months to a year). Recipients may pay off the loan in part or full with no penalties.
Closed Mortgage
This mortgage is explicit in its provision that the borrower is not allowed to repay, renegotiate, or refinance the loan before maturity.
Fixed Rate Mortgage
This type has locked interest rates protecting borrowers from market rate fluctuations. To quickly pay off the loan, lenders can offer prepayment options.
Variable Rate Mortgage
Also known as adjustable rate mortgage (ARM), this mortgage offers alterable interest rates that are dependent on overall market behavior.
Capped Rate Mortgage
It is like the ARM-only that the lender guarantees a maximum or cap rate to secure the investment further. Since it is variable, borrowers can benefit from lower payments as rates decline.
Convertible Mortgage
This type offers an adjustable rate at the beginning of the loan but the mortgage is later converted into a fixed scheme.
Reverse Mortgage
This plan allows homeowners to borrow money against the equity of their home property. Consequently, they either receive a line of credit or fixed monthly payments from the lender. to convert their equity to its cash value. Payment of the loan is deferred until the homeowner sells or moves out of the property, or passes away. Most of the time, this mortgage supplements the retirement needs of senior homeowners, who must be at least 62 years old with a significant build-up of equity.
Why Invest in Mortgages?
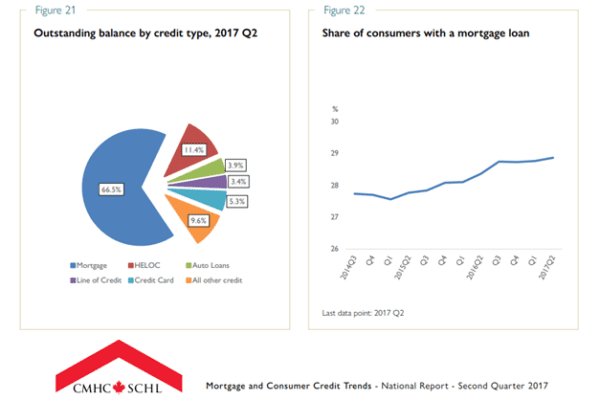
Investing in mortgages guarantees faster capital gains, which is why it is a venture that investors should consider. In fact, the latest report of CMHC noted a slight increase of mortgage holders in 2017. This trend indicates that more home buyers are using mortgages to own a home.
Key Benefits of Investing in Mortgages
- Guaranteed Financial Gains. Achieve faster return on investment by providing financial assistance to home loan borrowers. Investing in mortgages can efficiently increase your profits as real asset always increases in value over time.
- Reasonable Interests Rates. Borrowers with a good credit score can get low-interest rates, making the mortgage plan more attractive to them. These rates will save borrowers a substantial amount.
- Easy Mortgage Approval. Most of the time, lenders will quickly approve investors with excellent ratings. Faster loan approval will delight borrowers who will trust you even more.
- Wider Investment Reach. Your investment power and net worth will grow as your investments multiply, allowing you to add more properties to your portfolio quickly.
Investing in Mortgages is a Secure Venture
Many capitalists can grow their wealth with mortgage investments. For most investors, it is an excellent way to put money in real estate which appreciates in value over time. Moreover, as an investor, gaining a foothold in this field will ensure strengthen your investment power and will further diversify a strong portfolio.
Aside from your gains, investing in mortgages can be considered a service and kindness to people who need to purchase a new home but do not have large amounts of money on hand to pay for one. This alternative investment tool offers a variety of options to borrowers, allowing them to customize the plan according to their liking.
For inquiries, please contact the Canadian Mortgages Inc. Let us discuss your future venture into the real estate industry.